Environmental
Climate Change
Our approach to climate change
In recent years, the frequent occurrence of extreme weather such as heat waves and heavy rains has had a tremendous impact on the environment and society, as well as lifestyles and corporate activities.
It is hoped that frameworks for reducing greenhouse gases such as the 2015 Paris Agreement are accelerated, and initiatives addressing climate change are pursued as a responsibility to society by not only nations and governments, but also the private sector.
The Paris Agreement aims to suppress the rise in the earth’s average temperature to well below 2℃ and strives to contain the rise to 1.5℃. To achieve this goal, it aims to achieve a balance between the emission and absorption of man-made greenhouse gases in the latter half of this century. At COP27, the importance of achieving the 1.5°C target was included in the "Mitigation Work Plan," and countries are to strengthen their efforts to achieve the target. This could fundamentally alter the direction of social and economic activities for decades to come.
JLF and MLP strive to contribute to the shift toward a low-carbon society through initiatives including greenhouse gas reductions at the same time they adapt to natural disasters and other events resulting from climate change.
JLF and MLP have identified ESG materialities that JLF should address and have developed a recognition of how to address climate change.
To address climate change, detailed analysis has been performed and a strategy formulated, based on the TCFD recommendations.
<Targets (KPI)>
scope 1.2 GHG emission reduction targets:
・42% reduction by FY2030 (compared to FY2021)
・Net zero by FY2050
Expressing Support for TCFD (and participating in the TCFD Consortium)
In July 2021, Mitsui & Co., Logistics Partners Ltd. (MLP), JLF's asset manager, expressed its support for the TCFD recommendations and joined the TCFD Consortium, an organization of supporting companies in Japan.
The TCFD’s recommendations have been released to the public to advocate the ascertainment and disclosure of governance, strategy, metrics and targets and risk management by corporations, given the severe risks to the global economy posed by climate change.
JLF and MLP promote risk management and conduct information disclosures related to climate change based on the TCFD recommendations.
As set forth in the Environmental Management System (EMS) under the advancement and supervisory body, the Sustainability Advancement Organization, ESG initiatives are reported to and discussed with the Sustainability Promotion Liaison Meeting and MLP’s President and CEO and Board of Directors, and initiatives to address climate change are run and managed within the Environmental Management System (EMS).
Governance
JLF's asset manager, MLP, has established Guidelines for ESG Initiatives, which sets forth matters related to the advancement of sustainability, including addressing climate change. Our Sustainability Promotion Liaison Meeting is run and managed by our Finance & IR Department, with our President & CEO as Supervisor of Sustainability Promotion. Regular meetings are held once every three months, in general. There, participants review the Sustainability Policy and Goals and various sustainability initiatives considering circumstances in society and the state of operations at JLF.
Moreover, the Sustainability Promotion Liaison Meeting identifies ESG materialities, establishes and manages KPIs (action plans and targets), and reports to the Board of Directors.
Please refer to Sustainability Management for more information on the organization for advancing sustainability (including measures to address climate change), including an overview of the Sustainability Promotion Liaison Meeting.
Strategies
JLF and MLP identify risks and opportunities accompanying climate change, build an organization capable of conducting scenario-based analysis and reviews risks and opportunities annually. In doing so, JLF and MLP have divided the analysis into scenarios assuming a 1.5℃ temperature rise and a 4℃ rise to incorporate uncertainties arising from the progression of climate change into business strategies.
Details of the scenario analysis conducted by JLF in March 2025 can be found below.
<Scope of the scenario analysis>
Covers all properties owned by JLF.
<Scenarios considered>
| Publishing institution or organization | 1.5℃ scenario | 4℃ scenario | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transitional risks | IEA (International Energy Agency) |
IEA World Energy Outlook2024 NZE | IEA World Energy Outlook2024 STEPS |
| Physical risks | IPCC | IPCC AR6 SSP1-1.9 | IPCC AR6 SSP5-8.5 |
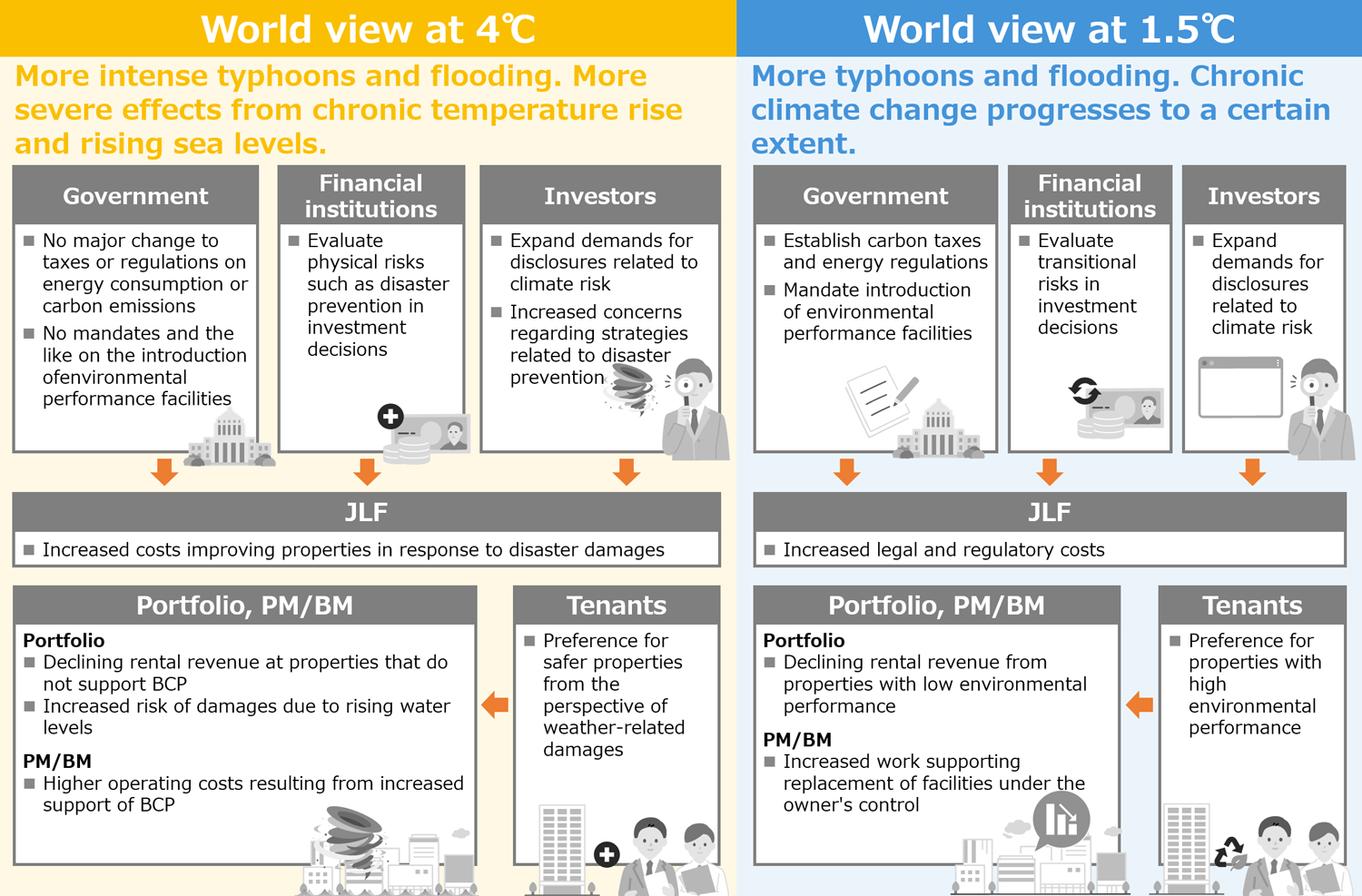
<Scenario-based world view according to JLF and MLP>
【1.5℃ scenario】
Under the 1.5℃ scenario, stringent regulatory and tax policies and the like are implemented to achieve a decarbonized society. As a result, emissions of greenhouse gases are on a declining trend and temperatures rise 1.5℃ compared to levels seen before the industrial revolution.
The introduction of an expensive carbon tax in Japan, aimed at suppressing CO2 emissions, results in taxes on CO2 emissions from portfolio properties. Additionally, stronger environmental regulations such as energy conservation standards lead to higher operating costs, such as renovations for compliance. Moreover, stronger regulations drive tenants to be more selective about the properties they occupy, leading to a decline in demand for properties with poor energy conservation performance compared to the competition. Furthermore, owners who possess many such properties may face higher fund-raising costs from investors and lenders. Meanwhile, increased frequency and intensity of damage due to climate change will be contained to a certain extent, keeping physical risks relatively low.
【4℃ scenario】
Under the 4℃ scenario, stringent regulatory and tax policies and the like are not implemented to address climate change. As a result, emissions of greenhouse gases continue to rise, and temperatures rise 4℃ compared to levels seen before the industrial revolution. Intensifying natural disasters, rising sea levels and increasingly severe weather cause an increase in property repair and maintenance costs, and the rise in average temperatures increases utilities expenses. These and other factors cause physical risks to rise, and products and services with superior BCP support enjoy increased competitiveness. Meanwhile, transitional risks remain low as governments fail to strengthen regulations.
<Climate-related risks/opportunities and response measures>
| Drivers related to real estate operations | Financial impact on JLF (JLF's challenges) | Timeline | Risk management, measures and initiatives (Strategy: Opportunities and direction) | KPI/KPIs and Targets | Financial Impact 4℃/1.5℃ |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transitional risks | Policy and Legal |
・Strengthened energy regulations (including reporting mandates) ・Possible introduction of carbon tax (carbon pricing) |
・Increased business expenses from the introduction of facilities to support reporting, payments to third-party vendors, etc. ・Increased costs from complying with future regulations, including renovation work and the introduction of renewable energy ・Increased tax burden in connection to property greenhouse gas emissions |
Medium term |
・Strengthen engagement with tenants and PM companies to support compliance with energy regulations ・Study matters such as energy conservation, power generation and switching power sources to reduce greenhouse gas emissions |
・scope 1.2 GHG emission reduction targets: ・Conduct ESG study sessions for all tenants (Once each year) ・Conduct ESG study sessions for all PM companies (Once each year) |
small impact | large impact |
| Techology |
・Delays in responding to the evolution in and adoption of renewable-energy and energy-conservation technologies and resulting loss of property competitiveness |
・Declining rental revenue due to relative underperformance in rent pricing and increased vacancy rates |
Medium term |
・Study introduction of high environmental-performance facilities to bolster property competitiveness |
・Consider energy conservation measures when acquiring external certifications |
small impact | large impact | |
| Market |
・Lower tenant demand and asset values at facilities with low environmental performance |
・Lower rental revenue, NOI and asset values due to falling rents and rising vacancy rates at facilities with low environmental performance |
Short term |
・Promote the introduction of green leases from the perspective of both operations and facility improvements to contribute to the environment through collaboration with tenants. |
・Implement green leases in 75% of portfolio as of the end of FY2025 ・Implement green leases at least 75% of portfolio until the end of FY2030 ・Exchange opinions on ESG with all tenants (Once each year) |
middle impact | large impact | |
| Reputation |
・Deterioration in procurement terms for market participants that have not responded to climate change risks |
・Increased fund-raising costs due to climate risks |
Short term |
・Study green finance and the like to leverage increased investment opportunities from institutional investors who focus on ESG investing |
・Acquire green building certifications in 95% of portfolio as of the end of FY2025 ・Acquire green building certifications at least 95% of portfolio until the end of FY2030 |
middle impact | large impact | |
| Physical risks | Acute |
・Risk of damage from intensifying typhoons and flooding |
・Higher repair and maintenance costs and insurance premiums ・Increased rental opportunity losses due to building destruction or damage |
Short term |
・Strengthen BCP support to enhance property competitiveness |
・Implement an initiative related to business continuity planning (BCP) |
large impact | middle impact |
| Chronic |
・Risk of damage from changes to meteorological patterns and rising sea levels, etc. |
・Occurrence of large-scale renovation costs ・Higher repair and maintenance costs resulting from increased operational burden from HVAC equipment |
Medium term |
・Implement planned repairs and maintenance at properties in response to changing meteorological patterns to enhance property competitiveness |
same as above | middle impact | middle impact | |
Strategy (including opportunities) given the scenario analysis
Under the 1.5℃ scenario, in the absence of investments aimed at improving property environmental performance, there is risk of a declining market presence and increasing impact on asset operations, such as tenant departures. Therefore, study ways to source renewable energy, such as switching existing power supply agreements and purchasing green energy certificates. Also, aim to enhance energy efficiency through energy conservation, energy generation, and the like.
Meanwhile, under the 4℃ scenario, real estate with greater resilience against damage from intensifying severe weather events would enjoy enhanced competitiveness. JLF believes the properties owned by JLF possess competitiveness in terms of safety and countermeasures against damage. Therefore, continue current initiatives while raising the bar even higher to maintain and enhance competitiveness in the market and increase business resilience.
Risk management
JLF and its asset manager, MLP, recognize climate-related risks as risks related to addressing global warming. Therefore, the President and CEO and the rest of the Sustainability Promotion Liaison Meeting identify climate-related risks and discuss matters including how to manage those risks.
The due diligence process when considering new asset acquisitions encompasses various studies of climate-related risks as a basis for deliberations at the investment committee and eventual investment decision at the Board of Directors. Specifically, water submersion levels according to various hazard maps are investigated in connection with the possibility of flooding or water submersion at the target property. Also, post-acquisition the Sustainability Promotion Liaison Meeting manages and monitors overall risk related to sustainability, including climate change risks.
Based on the risk management rules overseen by the Board of Directors, MLP annually identifies, monitors and evaluates risks in each workflow of each department and reports status thereof to the Board of Directors as appropriate. In connection with climate-related risks, risk categories are selected and evaluated in accordance with the workflows of each department, and risk mitigation measures are studied as necessary.
Measures and targets
Initiatives aimed at mitigating risk or realizing opportunities are, to the extent possible, assigned KPIs. Monitoring and goal-setting take place to manage these KPIs. Moreover, additional KPIs are studied where necessary to adapt to or mitigate climate change.
See below for targets and actual performance related to KPIs for greenhouse gas emissions.
<Greenhouse gas reduction targets>
scope 1.2 GHG emission reduction targets:
・ 42% reduction by FY2030 (compared to FY2021)
・ Net zero by FY2050
Green building commitment extends to existing buildings
JLF views the solving of environmental challenges such as climate change to be an important management challenge for JLF’s sustainable business activities and a business strategy aimed at realizing sustainability. That is why JLF invests in environmentally friendly properties (including development and redevelopment properties) and strives to enhance energy efficiency through environmental and energy-saving initiatives, including the installation of solar panels and the use of renewable energy for power generation. The aim is to build an environmentally friendly portfolio.
Targets (KPI)
Environmental performance data coverage rate
JLF and MLP aim for 100% coverage of environmental performance data as a medium- to long-term target out to FY2030.
Rate of conversion to LED lighting
JLF intends to promote the use of LEDs in the properties it owns, and the initial target of 80% has been achieved. Going forward, JLF aims to maintain the 80% LED conversion until FY2030, and will continue to promote initiatives to improve environmental performance from the time of acquisition.
Water saving
JLF promotes water conservation initiatives through ESG awareness activities for each tenant, with the goal of keeping or decreasing water use intensity compared to FY2018.

